A Guide to Understanding Your Customers
In today’s customer-centric world, brands must understand their audience at every touchpoint. User journey mapping is a strategic tool that helps marketers visualize and improve the user experience by breaking down the customer journey into actionable insights. By identifying key interactions, emotions, and expectations, brands can craft more personalized, engaging experiences that drive conversions and loyalty.
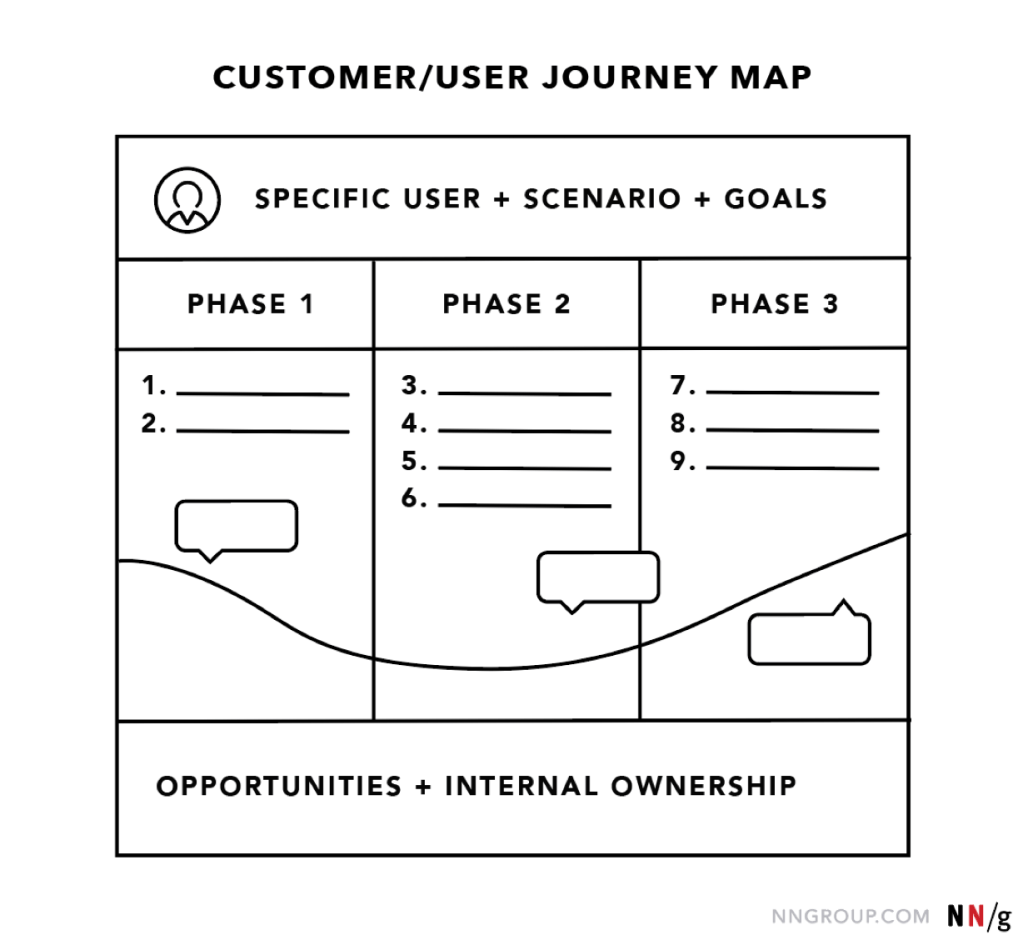
Key Components of a User Journey Map
Journey maps can take various forms, but they all share these five fundamental elements:
- Actor
- Scenario + Expectations
- Journey Phases
- Actions, Mindsets, and Emotions
- Opportunities
1. Actor
The actor represents the persona or user experiencing the journey. The journey map is created from their point of view, aligning with their behaviors, needs, and expectations.
Example: A university creating a journey map for student enrollment might define the actor as a prospective student researching degree programs. A separate journey map would be needed for faculty members seeking to onboard new courses.
2. Scenario + Expectations
The scenario describes the context of the journey, including the user’s goals and expectations.
Example: A customer looking to switch mobile plans wants a seamless process, expecting clear pricing, easy plan comparisons, and quick activation. If the experience is frustrating or unclear, they might abandon the switch entirely.
Journey maps work best for scenarios that:
- Involve a sequence of events (e.g., booking a vacation, buying a home)
- Describe a process (e.g., applying for a loan, onboarding new software)
- Span multiple channels (e.g., researching a product online before purchasing in-store)
3. Journey Phases
Journey phases are the high-level stages users go through. These vary based on the industry and scenario.
Examples:
- E-commerce (Buying Bluetooth Speakers): Discover → Research → Try → Purchase → Use → Seek Support
- Luxury Purchase (Buying a Car): Engagement → Education → Research → Evaluation → Justification
- B2B Purchase (Rolling Out Internal Software): Awareness → Purchase → Adoption → Retention → Expansion → Advocacy
Each phase allows marketers to optimize interactions and improve customer experience at every step.
4. Actions, Mindsets, and Emotions
This component captures what the user is doing, thinking, and feeling throughout their journey.
- Actions: The steps users take in each phase.
- Mindsets: Their motivations, questions, and information needs.
- Emotions: A visual representation of emotional highs and lows throughout the journey.
Example: A customer buying a new skincare product online:
- Discover Phase: Browsing Instagram ads → Curious about ingredients → Excited
- Research Phase: Reading product reviews → Wondering if it suits their skin type → Hesitant
- Purchase Phase: Comparing prices on different websites → Concerned about return policy → Nervous
- Use Phase: Trying the product → Noticing improvements → Satisfied
- Support Phase: Contacting customer service for a refund → Experiencing long wait times → Frustrated
By mapping out these emotions, brands can identify pain points and improve touchpoints to enhance customer satisfaction.
5. Opportunities
Opportunities are insights gained from journey mapping that highlight areas for improvement and innovation.
Example: If many customers drop off during the research phase due to unclear product information, a brand can add comparison charts, FAQs, or live chat support to address their concerns and improve conversions.
Questions to ask when identifying opportunities:
- What friction points can be removed?
- Who is responsible for implementing changes?
- Where are the biggest opportunities for engagement?
- How will success be measured?

Conclusion
User journey mapping is a powerful tool for understanding customer behavior and optimizing the experience across every touchpoint. By mapping actors, scenarios, phases, actions, emotions, and opportunities, brands can make data-driven decisions that enhance engagement, improve conversions, and foster long-term customer loyalty. Investing time in journey mapping isn’t just about fixing problems—it’s about creating seamless, enjoyable experiences that turn customers into brand advocates.
Ready to start your journey mapping? Dive in and transform how your brand connects with its customers today!
Leave a comment