Introduction

Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are the backbone of many large organizations. They connect finance, operations, IT, and even marketing into a unified platform that drives efficiency and visibility. Yet, for many enterprises, legacy systems are holding them back. Processes become fragmented, data silos slow down decision-making, and compliance risks grow with scale.
Planning for a new ERP is not a simple software upgrade. It is a transformation that touches every part of the business. This guide walks through what ERP is, how it helps solve business problems, and how leaders can successfully navigate the process of selecting, budgeting, and implementing the right solution.
What is ERP and Why It Matters
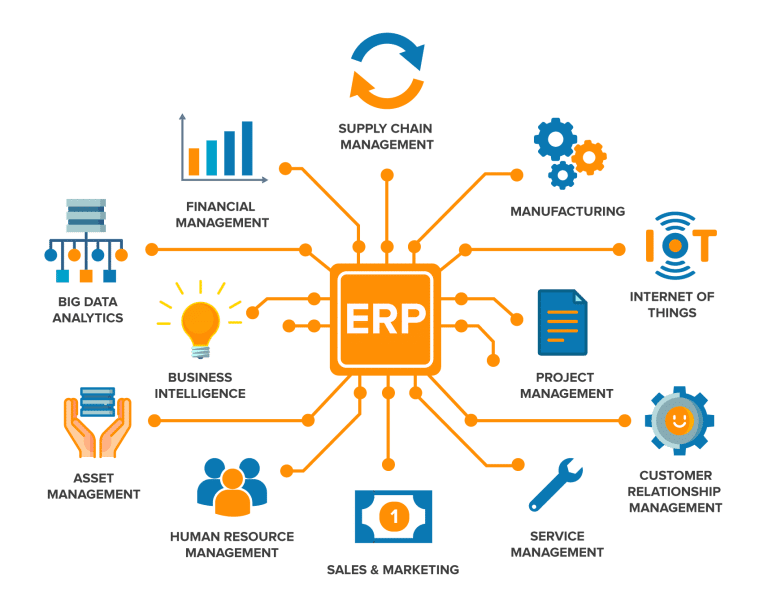
ERP, or Enterprise Resource Planning, is a centralized system that integrates core business functions into one platform. Instead of running multiple disconnected tools, ERP gives leaders a single source of truth.
ERP can solve problems across multiple functions:
- Finance
- Reduces manual reconciliations and reporting errors.
- Improves forecasting and cash flow management.
- Supports global compliance and audit readiness.
- IT
- Consolidates outdated legacy systems.
- Improves data governance and system security.
- Reduces costs by standardizing platforms across business units.
- Marketing and Sales
- Connects customer data with supply and operations.
- Enables better campaign targeting and ROI measurement.
- Aligns demand planning with marketing activities.
In short, ERP is both a data hub and a process optimizer, helping enterprises shift from siloed operations to an integrated, future-ready model.
Why Now? The Case for ERP Modernization
Enterprises often delay ERP modernization because of the cost and complexity. However, waiting too long can create bigger risks.
Key drivers for upgrading ERP include:
- Global expansion and the need for unified systems.
- Compliance requirements across multiple markets.
- Digital transformation initiatives that require real-time data.
- The need for automation and AI-driven insights.
- Rising maintenance costs of outdated systems.
Modern ERP is not just about efficiency. It delivers competitive advantage by giving leaders visibility across the enterprise and enabling data-driven decision-making.
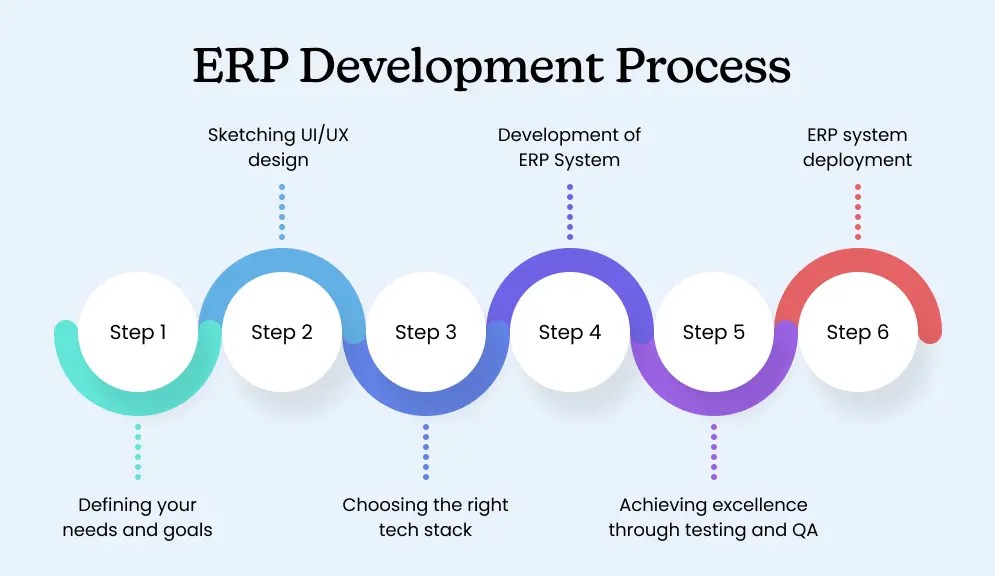
The ERP Planning Process
Before rushing into vendor selection, enterprises should create a structured planning process.
Steps to follow:
- Define business objectives: efficiency, compliance, customer experience, or cost reduction.
- Map current processes: identify inefficiencies, redundancies, and manual workarounds.
- Build a cross-functional steering team: include finance, IT, operations, HR, and marketing.
- Create a change management strategy: plan for training, adoption, and communication.
A strong planning phase ensures ERP is not just an IT initiative but a company-wide transformation.
ERP System Solutions and Options
Enterprises have multiple ERP options, ranging from global Tier 1 solutions to mid-market and industry-specific platforms.
Tier 1 Enterprise Solutions:
- SAP S/4HANA: Designed for large global enterprises, strong in finance and manufacturing.
- Oracle Fusion and NetSuite: Cloud-based with deep financial functionality.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365: Flexible modules and strong integration with Microsoft products.
Tier 2 Mid-to-Large Scale Solutions:
- Infor: Manufacturing, supply chain, and distribution focus.
- Workday: HR and finance-centric with a strong cloud reputation.
- Epicor: Suited for industrial and mid-size organizations.
Industry or Niche Solutions:
- Odoo: Open-source and highly modular.
- Acumatica: Cloud ERP popular with mid-size and fast-growing enterprises.
When selecting a system, consider:
- Industry alignment.
- Integration with current systems.
- AI and automation capabilities.
- Vendor support and partner ecosystem.
- Scalability for future growth.
Cost Considerations and Budgeting
ERP is a major financial investment. Understanding the cost categories up front helps prevent budget overruns.
Initial Costs:
- Licensing or subscription fees.
- Implementation and consulting services.
- Data migration and system configuration.
Ongoing Costs:
- Cloud subscriptions or maintenance.
- Vendor support and security updates.
- Training and onboarding new staff.
Hidden Costs:
- Downtime during implementation.
- Integration challenges with legacy tools.
- Resistance to change and adoption issues.
ERP should not be viewed as a one-time cost but as a long-term ROI investment. Done right, it reduces waste, improves forecasting, and supports better business outcomes.
Navigating the Implementation Journey
Implementation is often the most complex part of ERP. Enterprises should take a phased approach:
- Discovery and Planning: Scope requirements, set governance structures, and outline timelines.
- Vendor Selection and Proof of Concept: Test the system against real scenarios.
- Implementation and Data Migration: Move core systems and ensure data quality.
- Training and Change Management: Prepare teams for new workflows.
- Optimization and Continuous Improvement: Add new modules, improve automation, and fine-tune reporting.
ERP implementation should be treated as an ongoing journey, not a one-time project.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Many ERP projects fail due to poor planning or execution. The most common pitfalls include:
- Underestimating total cost of ownership.
- Over-customizing the system, making future upgrades harder.
- Weak executive sponsorship and lack of accountability.
- Neglecting user training and adoption support.
Avoiding these mistakes can mean the difference between ERP success and costly failure.
Conclusion
Selecting and implementing an ERP system is one of the most significant decisions an enterprise can make. It is not just a software purchase, but a strategic transformation that impacts finance, IT, marketing, and beyond.
By defining clear objectives, carefully evaluating solutions, budgeting effectively, and supporting change management, organizations can turn ERP into a growth enabler.
The first step is simple but powerful: conduct an internal ERP readiness and ROI assessment to understand your organization’s needs before moving forward.
Leave a comment